You have no items in your shopping cart.
- Home /
- Blog /
- Knowledge Base /
- Cannabidiol
Cannabidiol
This entry was posted on March 26, 2018 by admin.
|
|
This article's lead section may not adequately summarize its contents. To comply with Wikipedia's lead section guidelines, please consider modifying the lead to provide an accessible overview of the article's key points in such a way that it can stand on its own as a concise version of the article. (discuss). (January 2018)
|
| Part of a series on |
| Cannabis |
|---|
 |
|
Chemistry
|
Cannabidiol (INN;[3] abbreviated as: CBD) is one of at least 113 active cannabinoids identified in cannabis.[4][5] It is a major phytocannabinoid, accounting for up to 40% of the plant's extract.[6]
CBD does not appear to have any psychoactive effects such as those caused by tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and it may have a downregulating impact on disordered thinking and anxiety.[7]
Medical uses
Pain associated with multiple sclerosis
Nabiximols (USAN, trade name Sativex) is an aerosolized mist for oral administration containing a near 1:1 ratio of CBD and THC. The drug was approved by Canadian authorities in 2005 to alleviate pain associated with multiple sclerosis.[8][9]
Research
Addiction treatment
In 2015 a case study on CBD and addictive use of marijuana was published. A bipolar man who had a daily marijuana habit was given CBD along with his regimen of medication and reported less anxiety and no marijuana use.[10] A 2015 systematic review of studies on CBD and addiction (five on humans, nine on animals) found that CBD acts on neurotransmittors involved in addiction; animal studies showed some relation in opioid and psychostimulant addiction and human studies showed beneficial effects for tobacco and cannabis dependence. However, the anti-addictive properties displayed might be due to CBD's protective effect on stress and neurotoxicity, the review also mentions the need for more research.[11]
Anti-inflammatory
A number of studies on CBD indicate that it may be useful in treating inflammation caused by a variety of conditions. A 2012 study published in the European Journal of Pharmacology concluded that cannabidiol has anti-inflammatory effects in a murine model of acute lung injury and that this effect is most likely associated with an increase in the extracellular adenosine offer and signaling through adenosine A2A receptor.[12] Another 2012 study found similar anti-inflammatory effects from an even smaller dose of CBD when treating acute pancreatitis in mice.[13] These conclusions support the findings of earlier studies like a 2006 investigation of CBD that found it could be used effectively as an oral therapeutic agent for chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain.[14]
Epilepsy
Anecdotal reports and early studies suggested that CBD may be of value in treating epilepsy, but the quality of the studies was too poor to draw definitive conclusions.[15][16] A 2014 Cochrane review included four randomized controlled trials, but all were of poor quality.[17] A double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled study of CBD oil on treating Dravet syndrome, a rare form of epilepsy that begins in infancy and is difficult to treat,[18] was conducted in 2017 and found that CBD oil significantly reduced the number of seizures with a dosing of 20mg/kg. However, it also caused increased diarrhea, vomiting, fevers, fatigue, abnormal liver function tests (LFTs), and somnolence. The LFTs showed elevated ALT and AST up to three times of normal, but only in the patients also taking valporate. The study already suggests that this might be an interaction of valporate and CBD. The abnormal LFT normalized during the trial in the patients who kept taking CBD.[19]
GW Pharmaceuticals is seeking FDA approval to market a liquid formulation of pure plant-derived CBD, under the trade name Epidiolex (containing 99% cannabidiol and less than 0.10% Δ9-THC) as a treatment for Dravet syndrome. Epidiolex was granted fast-track status[20][21][22] and orphan drug status in the United States for treatment of Dravet syndrome in July 2015.[23][24]
Adverse effects
CBD safety in humans has been studied in multiple small studies, suggesting that it is well tolerated at doses of up to 1,500 mg/day given orally or 30 mg given intravenously.[25] Daily doses of CBD (700 mg) for 6 weeks did not induce any toxicity in patients being treated for Huntington's disease.[26]
Interactions
There is preclinical evidence to suggest that cannabidiol may reduce THC clearance, modestly increasing THC's plasma concentrations resulting in a greater amount of THC available to receptors, increasing the effect of THC in a dose-dependent manner.[27][28] Despite this, the available evidence in humans suggests no significant effect of CBD on THC plasma levels.[29]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Cannabidiol has very low affinity for the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors but acts as an indirect antagonist of these receptors.[30][31] It may potentiate THC's effects by increasing CB1 receptor density or through another CB1 receptor-related mechanism.[32] Cannabidiol may also extend the duration of the effects of THC via inhibition of the cytochrome P450, CYP3A and CYP2C enzymes.[33][unreliable source?]
Cannabidiol has been found to act as an antagonist of GPR55, a G protein-coupled receptor and putative cannabinoid receptor that is expressed in the caudate nucleus and putamen in the brain.[34] It has also been shown to act as a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist,[35] and this action may be involved in the antidepressant,[36][37] anxiolytic,[37][38] and neuroprotective[39][40] effects of cannabidiol. It is an allosteric modulator of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors as well.[41] Cannabidiol's pharmacological effects have additionally been attributed to PPARγ agonism and intracellular calcium release.[6]
Research suggests that CBD may exert some of its pharmacological action through its inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which may in turn increase the levels of endocannabinoids, such as anandamide, produced by the body.[6] It has also been speculated that some of the metabolites of CBD have pharmacological effects that contribute to the biological activity of CBD.[42]
Recently, cannabidiol has been identified as a novel inverse agonist of the GPR12.[43]
Chemistry
Cannabidiol is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as pentane. At room temperature, it is a colorless crystalline solid.[44] In strongly basic media and the presence of air, it is oxidized to a quinone.[45] Under acidic conditions it cyclizes to THC.[46] The synthesis of cannabidiol has been accomplished by several research groups.[47][48][49]
Biosynthesis
Cannabis produces CBD-carboxylic acid through the same metabolic pathway as THC, until the last step, where CBDA synthase performs catalysis instead of THCA synthase.[50]
Cannabidiol and THC biosynthesis[51]
Isomerism
| 7 double bond isomers and their 30 stereoisomers | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formal numbering | Terpenoid numbering | Number of stereoisomers | Natural occurrence | Convention on Psychotropic Substances Schedule | Structure | |||
| Short name | Chiral centers | Full name | Short name | Chiral centers | ||||
| Δ5-cannabidiol | 1 and 3 | 2-(6-isopropenyl-3-methyl-5-cyclohexen-1-yl)-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol | Δ4-cannabidiol | 1 and 3 | 4 | No | unscheduled | 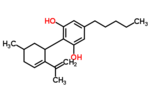 |
| Δ4-cannabidiol | 1, 3 and 6 | 2-(6-isopropenyl-3-methyl-4-cyclohexen-1-yl)-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol | Δ5-cannabidiol | 1, 3 and 4 | 8 | No | unscheduled |  |
| Δ3-cannabidiol | 1 and 6 | 2-(6-isopropenyl-3-methyl-3-cyclohexen-1-yl)-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol | Δ6-cannabidiol | 3 and 4 | 4 | ? | unscheduled |  |
| Δ3,7-cannabidiol | 1 and 6 | 2-(6-isopropenyl-3-methylenecyclohex-1-yl)-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol | Δ1,7-cannabidiol | 3 and 4 | 4 | No | unscheduled | 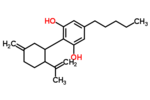 |
| Δ2-cannabidiol | 1 and 6 | 2-(6-isopropenyl-3-methyl-2-cyclohexen-1-yl)-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol | Δ1-cannabidiol | 3 and 4 | 4 | Yes | unscheduled |  |
| Δ1-cannabidiol | 3 and 6 | 2-(6-isopropenyl-3-methyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol | Δ2-cannabidiol | 1 and 4 | 4 | No | unscheduled | 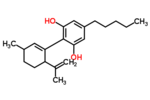 |
| Δ6-cannabidiol | 3 | 2-(6-isopropenyl-3-methyl-6-cyclohexen-1-yl)-5-pentyl-1,3-benzenediol | Δ3-cannabidiol | 1 | 2 | No | unscheduled | 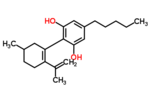 |
CBD products on the market
CBD Edibles Online
If you’re looking for edibles for sale online, CBD Goldline has one of the broadest selections available. From CBD gummies and honey to capsules. Goldline CBD brand is proud to offer a variety of products that will work for just about anyone. Every batch of our CBD oil tincture edibles gets tested at an independent lab to ensure an excellent standard of quality. Our customers trust us for consistent doses of cannabidiol in a delicious, snackable format. Contact us if you have any additional questions about our edible CBD, or shop online today!
CBD Vape Oil and Vape Pens
If you’re new to the idea of using CBD as a health supplement, you may be open to the idea of vaping CBD oil or oral ingestion. Many users prefer to vape or inhale cannabidiol as a form of consumption of the CBD. Other users prefer edible CBD treats or gummies, whatever your preference may be, you may find it on the Best CBD Products Review website. From CBD vape pens and tinctures to dog treats infused with CBD.
Natural sources
Selective breeding by growers in the USA dramatically lowered the CBD content of cannabis; their customers preferred varietals that were more mind-altering due to a higher THC, lower CBD content.To meet the demands of medical cannabis patients, growers are currently developing more CBD-dominant strains.
Legal status
CBD does not appear to have any psychoactive ("high") effects such as those caused by ∆9-THC in marijuana, but may have anti-anxiety and anti-psychotic effects.[7] As the legal landscape and understanding about the differences in medical cannabinoids unfolds, it will be increasingly important to distinguish "medical marijuana" (with noted varying degrees of psychotropic effects and deficits in executive function) – from "medical CBD".[7][57]
Various breeds/strains of "medical marijuana" are found to have a significant variety in the ratios of CBD-to-THC and are known to contain other non-psychotropic cannabinoids.[58] However it is only the amount of ∆9-THC that chemically gives a legal determination as to whether the plant material(s) used for the purposes of extracting CBD are considered hemp, or considered marijuana.[citation needed]
Any psychoactive marijuana, regardless of its CBD content, is derived from the flower (or bud) of the genus Cannabis. Non-psychoactive hemp (also commonly-termed industrial hemp), regardless of its CBD content, is any part of the cannabis plant, whether growing or not, containing a ∆-9 tetrahydrocannabinol concentration of no more than three-tenths of one percent (0.3%) on a dry weight basis. Certain standards are required for the legal growth and production of hemp. The Colorado Industrial Hemp Program registers growers of industrial hemp and samples crops to verify that the THC concentration does not exceed 0.3% on dry weight basis.[59]
United States
In the United States, cannabidiol is a Schedule I drug under the Controlled Substances Act. This means that production, distribution and possession of CBD is illegal under federal law. In 2016, the Drug Enforcement Administration added "marihuana extracts" to the list of Schedule I drugs, which it defined as "an extract containing one or more cannabinoids that has been derived from any plant of the genus Cannabis, other than the separated resin (whether crude or purified) obtained from the plant."[61] Previously, CBD had simply been considered "marijuana," which is also a Schedule I drug.[60][62]
A CNN program that featured Charlotte's Web cannabis in 2013 brought increased attention to the use of CBD in the treatment of seizure disorders. Since then, 17 states have passed laws to allow for the use of CBD products (not exceeding a specified concentration of THC) for the treatment of certain medical conditions. This is in addition to the 29 states that have passed comprehensive medical cannabis laws, which allow for the use of cannabis products with no restrictions on THC content. Of these 29 states, 8 have legalized the use and sale of cannabis products without requirement for a doctor's recommendation.
Although most states restrict the use of CBD products to certain medical conditions, manufacturers of CBD claim their products are derived from industrial hemp, and therefore legal for anyone to use. A number of these manufacturers ship CBD products to all 50 states, which the federal government has so far not intervened in. CBD is also openly sold in head shops and health food stores in some states where such sales have not been explicitly legalized.
This entry was posted in Knowledge Base on March 26, 2018 by admin. ← Previous Post Next Post →